Research
Machine learning is a dynamic and multifaceted field that encompasses various research areas, each contributing to the broader goal of creating intelligent systems capable of learning, adapting, and evolving. Below, we explore the major research areas that define the landscape of machine learning.
AI Theory
AI Theory is the foundational bedrock of artificial intelligence, focusing on the mathematical and computational principles that govern the behavior and capabilities of AI systems. It explores algorithms, complexity, logic, and statistical methods to understand how machines can mimic human intelligence. Research in AI Theory seeks to create models that can explain, predict, and enhance the performance of AI, ensuring robustness, efficiency, and ethical considerations.
Democratizing AI through Multi-Hop Federated Learning Over-the-Air
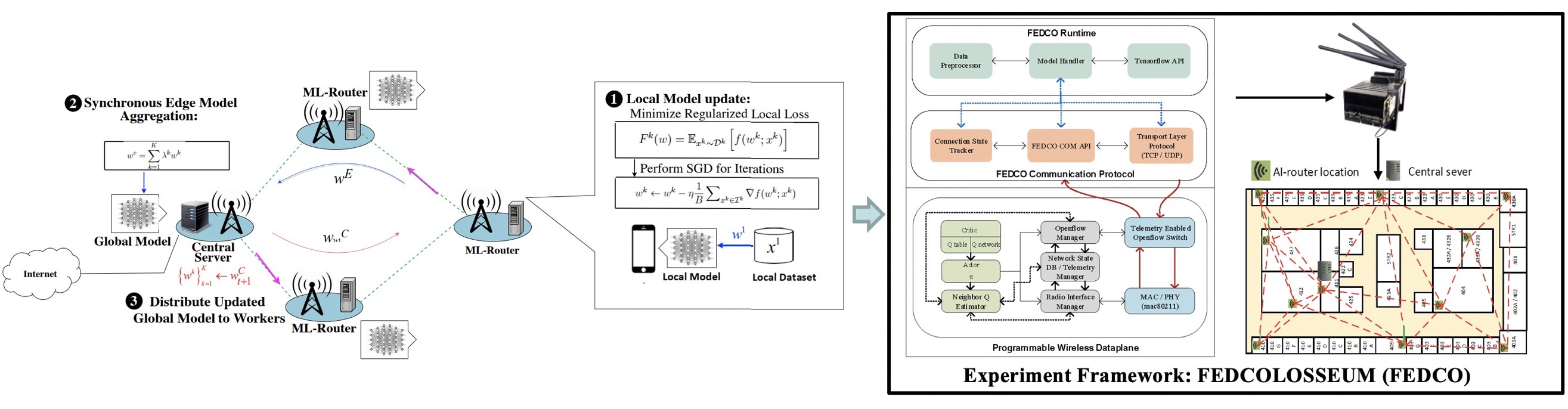
Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a key technology for enabling next-generation privacy-preserving AI at-scale, where a large number of edge devices, e.g., mobile phones, collaboratively learn a shared global model while keeping their data locally to prevent privacy leakage. Enabling FL over wireless multi-hop networks, such as wireless community mesh networks and wireless Internet over satellite constellations, not only can augment AI experiences for urban mobile users, but also can democratize AI and make it accessible in a low-cost manner to everyone, including people in low-income communities, rural areas, under-developed regions, and disaster areas. The overall objective of this project is to develop a novel wireless multi-hop FL system with guaranteed stability, high accuracy and fast convergence speed. This project is expected to advance the design of distributed deep learning (DL) systems, to promote the understanding of the strong synergy between distributed computing and distributed networking, and to bridge the gap between the theoretical foundations of distributed DL and its real-life applications. The project will also provide unique interdisciplinary training opportunities for graduate and undergraduate students through both research work and related courses that the PIs will develop and offer.
Recent publications:
- EdgeML: Towards network-accelerated federated learning over wireless edge
- Toward scalable and robust AIoT via decentralized federated learning
- Local learning matters: Rethinking data heterogeneity in federated learning
- MutualNet: Adaptive ConvNet via Mutual Learning From Different Model Configurations
- Fedair: Towards multi-hop federated learning over-the-air
- Delay-Optimal Traffic Engineering through Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Computer Vision
Computer Vision is the science of enabling machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual data. It involves the automatic extraction, analysis, and understanding of useful information from a single image or a sequence of images. Applications range from facial recognition and medical image analysis to autonomous driving and industrial inspection. Computer Vision combines techniques from image processing, pattern recognition, geometry, and machine learning to replicate the human ability to perceive and interpret the visual world.
Video Understanding for Activities of Daily Living
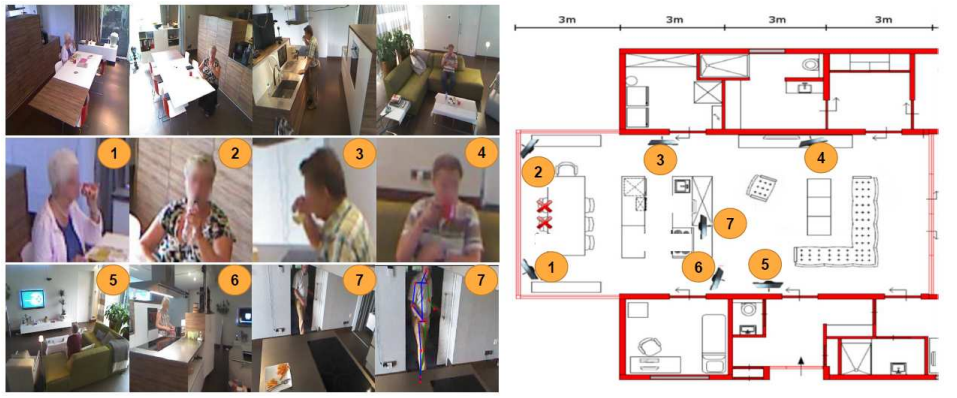
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) encompass the fundamental and routine tasks that individuals perform as part of their daily lives. While most research in the field of action recognition focuses on actions seen in web videos, ADL are often times more "boring", consisting of actions such as walk, drink water, watch TV. These everyday tasks are not commonly available in internet sources but are of paramount importance, especially in healthcare, gerontology, rehabilitation, and long-term care settings. ADL poses unique challenges compared to web videos that must be considered when designing models for understanding ADL videos.
Recent publications:
- Seeing the Pose in the Pixels: Learning Pose-Aware Representations in Vision Transformers
- Toyota smarthome: Real-world activities of daily living
Tools:
Can Multi-view Improve Aerial Visual Perception?
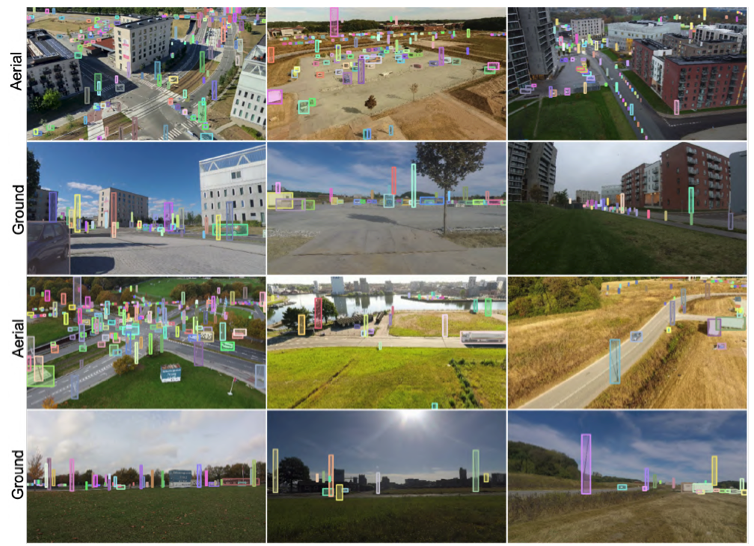

Using aerial footage from UAVs or drones for object detection and tracking is crucial in various applications, including autonomous driving, environmental monitoring, infrastructure inspection, and creating secure communities. Small items in a large background, occlusions, complicated backgrounds, and lighting and shadow fluctuations make this work difficult. Computer vision has advanced rapidly with data-hungry DNN models, but aerial data has not. Can we improve aerial view object recognition by adding other viewpoints with better visual perception?
Incorporating human pose into vision-language models
Vision language models (such as CLIP) are trained on image-text pairs and exhibit impressive performance on many tasks, such as zero shot image classification and object detection. We have also seen that these models, trained on image-text pairs, can be adapted to videos to perform zero shot video understanding. However, these adaptations only consider the RGB and language modalities, which are not enough for many video understanding tasks (e.g. action recognition for activities of daily living videos).
Data Science
Data Science is the interdisciplinary field that uses scientific methods, algorithms, processes, and systems to extract knowledge and insights from structured and unstructured data. It encompasses statistics, data mining, machine learning, and big data technologies to analyze and interpret complex data. Data Science is vital in various industries, including healthcare, finance, retail, and government, enabling data-driven decision-making, predictive analytics, and actionable insights.
SocialBit: Establishing the Accuracy of a Wearable Sensor to Detect Social Interactions after Stroke
Stroke survivors are vulnerable to reduced social interactions. Reduced interactions are related to worse physical recovery after stroke. Enhancing social interactions after stroke may be one of the most powerful strategies to improve stroke recovery. A new wearable social sensor, SocialBit can detect audio signatures of social interactions in real-world settings.
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. It aims to enable machines to understand, interpret, generate, and respond to human language in a valuable way. NLP involves several challenges, including language modeling, parsing, sentiment analysis, machine translation, and speech recognition. It has diverse applications such as chatbots, search engines, and language translation services.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment. The agent receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties and aims to maximize cumulative rewards over time. RL is inspired by behavioral psychology and has applications in various domains, including robotics, game playing, finance, and healthcare. Research in RL explores algorithms, exploration-exploitation trade-offs, multi-agent systems, and real-world implementations.
Example-based Reinforcement Learning
A significant hurdle in the successful application of reinforcement learning (RL) across various domains is the voracious appetite for data. The performance of RL models hinges heavily on having access to copious amounts of high-quality data. However, in practical terms, obtaining such data proves to be a formidable and costly task, thereby complicating the assurance of optimal RL model performance. Interactive RL scenarios contend with limited interactions, influenced by factors like exorbitant costs or financial constraints in real-world settings such as production, healthcare, transportation, finance, or trade. The scarcity of interactions gives rise to apprehensions regarding the generalizability, reliability, and safety of deployed systems, consequently eroding their trustworthiness. The project endeavors to surmount this pivotal challenge through a multifaceted approach, encompassing example-based reinforcement learning, graph inference to forge new knowledge representations, multimodal feedback to enhance data quality, and an exploration into the impact of human involvement on data efficiency.
Recent publications:
- Learning sparse evidence-driven interpretation to understand deep reinforcement learning agents
- Efficient practice for deep reinforcement learning
- Relevant experiences in replay buffer
- Deep reinforcement learning monitor for snapshot recording
Time Series
Time Series analysis involves the study of ordered, often temporal data points. It is used to analyze trends, seasonality, and patterns in data over time. Time Series analysis is crucial in various fields such as economics, finance, environmental science, and healthcare. It helps in forecasting future values, understanding underlying structures, and making informed decisions. Techniques in Time Series analysis include statistical methods, machine learning models, and frequency domain methods.
Semi-/Un-Supervised Learning for Medical Time Series
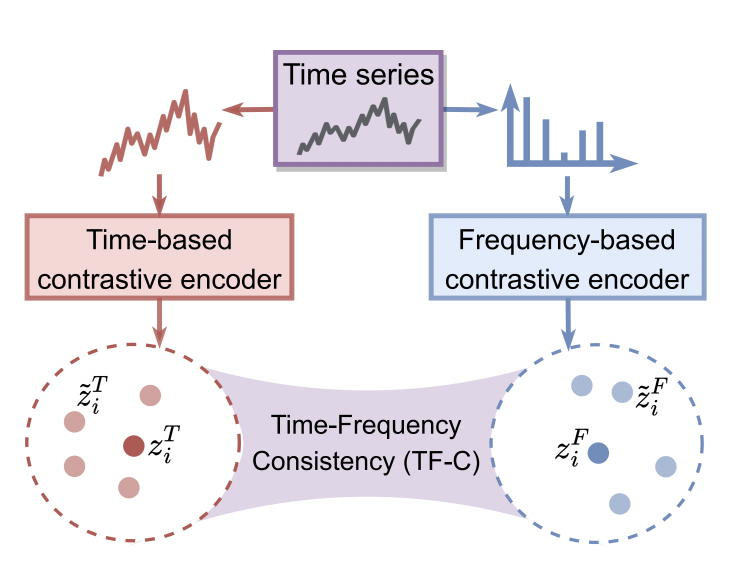
In healthcare, medical time series data like physiological signals and vital signs are crucial for patient care but often lack sufficient labels for analysis. The challenge is to interpret this complex data with limited labeled samples. We develop semi-supervised and unsupervised learning to tackle this issue, utilizing deep learning techniques to develop robust, interpretable models. These models effectively analyze medical time series data, aiding healthcare professionals in making better decisions when fully annotated data is scarce.
Recent publications:
- Self-Supervised Contrastive Pre-Training For Time Series via Time-Frequency Consistency
- Adversarial Variational Embedding for Robust Semi-supervised Learning
Deep Learning for Brain Signal Analysis
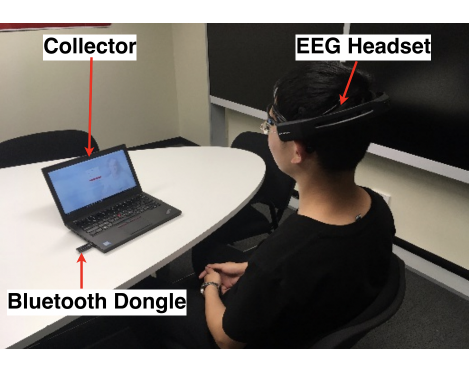
Deep learning have revolutionized the field of brain signal analysis by effectively captures high-level representations from noisy EEG data, offering promising advances in neuroscience and healthcare. This project dedicate to design a set of advanced deep learning algorithms and frameworks to seize the complex patterns within EEG signals. Our models enable more accurate classification performance, better monitoring of cognitive states, and improved patient diagnosis of neurological diseases, offering a significant upgrade over conventional methods.
Recent publications:
- A survey on deep learning-based non-invasive brain signals: recent advances and new frontiers
- MindID: Person Identification from Brain Waves through Attention-based Recurrent Neural Network
- Deep Learning for EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces
- Interpretable Sparsification of Brain Graphs: Better Practices and Effective Designs for Graph Neural Networks
Graph Nerual Networks for Relational Representation Learning
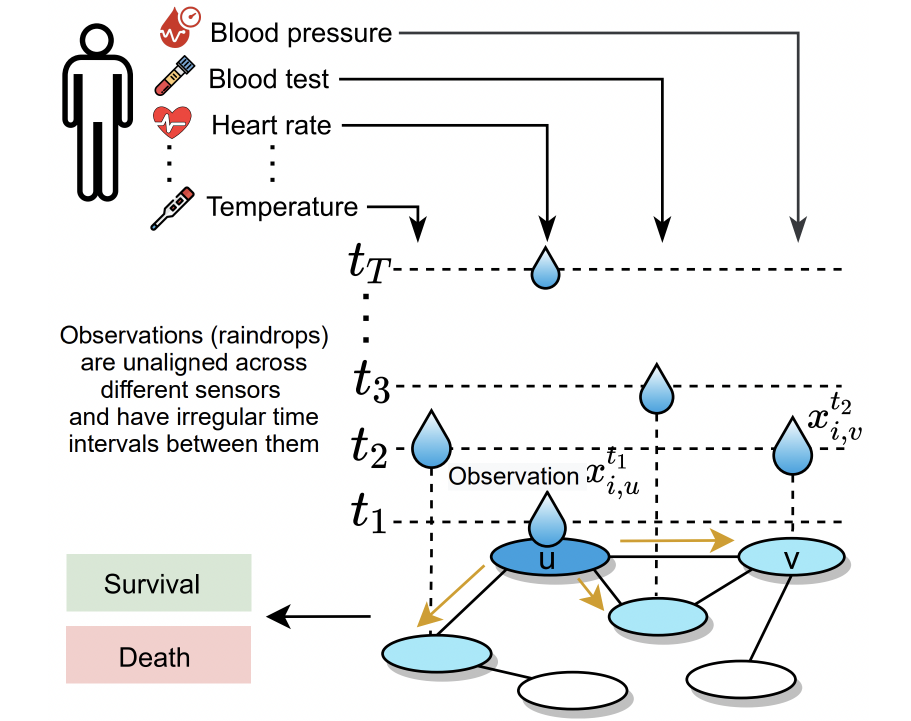
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool for learning on graph-structured data, capturing relationships that traditional neural networks often miss. The challenge in relational representation learning is to efficiently model and interpret complex, interdependent relationships within large datasets. Our research addresses this by applying GNNs to relational representation learning. Using innovative architectures and optimization techniques, these GNN-based models can automatically capture intricate dependencies within the data. Additionally, we extend this approach to uncover hidden relationships in informative time series data, such as vital signs in healthcare. In terms of cybersecurity, we've also created a model that defends GNNs against adversarial attacks.
Recent publications: